This is just a quick placeholder page with a link to the old Taylorcraft content on the previous webserver.

This is just a quick placeholder page with a link to the old Taylorcraft content on the previous webserver.

The current version of Kolab 3.4 for Debian 8 does not configure after installation.
|
1 2 3 4 |
deb http://obs.kolabsys.com/repositories/Kolab:/3.4/Debian_8.0/ ./ deb http://obs.kolabsys.com/repositories/Kolab:/3.4:/Updates/Debian_8.0/ ./ deb-src http://obs.kolabsys.com/repositories/Kolab:/3.4/Debian_8.0/ ./ deb-src http://obs.kolabsys.com/repositories/Kolab:/3.4:/Updates/Debian_8.0/ ./ |
Mostly because their package cyrus-imapd is compiled against perl-5.18 and Jessie ships with 5.20.
So the first thing that you have to do is build an -nmu package from their sources. Kolab sources require a single change to the file debian/cyrus-imapd.install.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
--- cyrus-imapd-2.5~dev2015021301/debian/cyrus-imapd.install 2015-10-18 19:08:45.805099123 +0200 +++ cyrus-imapd-2.5~dev2015021301/debian/cyrus-imapd.install-orig 2015-10-19 10:14:33.112279305 +0200 @@ -47,7 +47,7 @@ usr/lib/cyrus-imapd/sync_server usr/lib/cyrus-imapd/timsieved usr/lib/cyrus-imapd/tls_prune usr/lib/cyrus-imapd/unexpunge -usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/perl/5.20.2/* +usr/lib/perl* usr/sbin/* usr/share/icons/* usr/share/man/man1/* |
Another little gotcha is that setup-kolab ldap fails to configure because:
|
1 |
Use of literal control characters in variable names is deprecated at /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/dirsrv/perl/DSCreate.pm line 867. |
This patch gets it going:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
--- /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/dirsrv/perl/DSCreate.pm 2015-10-17 18:07:00.366900636 +0200 +++ /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/dirsrv/perl/DSCreate.pm~ 2015-03-09 09:54:50.000000000 +0100 @@ -864,7 +864,7 @@ sub setDefaults { } if (!defined($inf->{slapd}->{sasl_path})) { - if ($ ne "linux") { + if ("nope" ne "linux") { $inf->{slapd}->{sasl_path} = "$inf->{General}->{prefix}/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/sasl2"; } } |
To check that the cyrus-imapd configuration is correct:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
root@mailserver:~# cyradm -u cyrus-admin localhost verify error:num=18:self signed certificate IMAP Password: <b>your password as configured</b> localhost> <b>^D</b> root@mailserver:~# |
Once self-signed certificates are working with cyradm it is safe to configure roundcube. The following stanzas must be present in /etc/roundcubemail/config.inc.php :
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
/ allow self signed $config['imap_conn_options'] = array( 'ssl' => array( 'verify_peer' => true, 'allow_self_signed' => true, 'peer_name' => 'mail.candlish.net', 'ciphers' => 'TLSv1+HIGH:!aNull:@STRENGTH', 'cafile' => '/etc/ssl/private/mail-candlish-net.pem', ), ); $config['smtp_conn_options'] = array( 'ssl' => array( 'verify_peer' => true, 'allow_self_signed' => true, 'peer_name' => 'mail.candlish.net', 'ciphers' => 'TLSv1+HIGH:!aNull:@STRENGTH', 'cafile' => '/etc/ssl/private/mail-candlish-net.pem', ), ); $config['managesieve_conn_options'] = array( 'ssl' => array( 'verify_peer' => true, 'allow_self_signed' => true, 'peer_name' => 'mail.candlish.net', 'ciphers' => 'TLSv1+HIGH:!aNull:@STRENGTH', 'cafile' => '/etc/ssl/private/mail-candlish-net.pem', ), |
The following text in /var/log/roundcube/errors is an indication that the cafiles are not readable:
|
1 |
[19-Oct-2015 00:37:10 Europe/Berlin] PHP Warning: failed loading cafile stream: `/etc/ssl/private/mail-candlish-net.pem' in /usr/share/roundcubemail/program/lib/Roundcube/rcube_imap_generic.php on line 913 |
To make the cafile is readable it should be set chgrp ssl-cert and the user www-data should be a member of the ssl-cert group.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
root@mailserver:/etc/ssl/private# ls -l total 32 -rw-r----- 1 root ssl-cert 3111 Jan 7 2015 cyrus-imapd.pem -rw-r--r-- 1 root ssl-cert 1513 Oct 18 22:47 mail-candlish-net.crt -rw-r----- 1 root ssl-cert 1708 Oct 18 22:47 mail-candlish-net.key -rw-r----- 1 root ssl-cert 3221 Oct 19 00:15 mail-candlish-net.pem -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1513 Oct 18 23:05 mailserver-bed-lum.crt -rw-r----- 1 root root 1704 Oct 18 23:05 mailserver-bed-lum.key -rw-r----- 1 root root 3217 Oct 19 00:15 mailserver-bed-lum.pem -rw-r----- 1 root ssl-cert 1704 Jan 7 2015 ssl-cert-snakeoil.key root@mailserver:/etc/ssl/private# grep ssl-cert /etc/group ssl-cert:x:105:cyrus,www-data root@mailserver:/etc/ssl/private# |
Then it should be possible to log-in to the roundcube web client.
REF:
https://docs.kolab.org/upgrade-guide/kolab-3.4.html
https://docs.kolab.org/installation-guide/debian-community.html
https://docs.kolab.org/administrator-guide/using-the-kolab-command-line.htm
lhttps://docs.kolab.org/administrator-guide/setup-kolab-cli-reference.html
https://git.kolab.org/T492
My February '95 Statistics 462 midterm notes. In 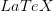 .
.
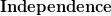
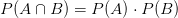
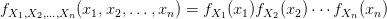
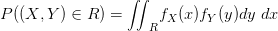
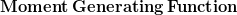
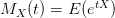

![$ Var(X)=M_{X}^{''}(0)-[M_{X}^{'}(0)]^2 $ $ Var(X)=M_{X}^{''}(0)-[M_{X}^{'}(0)]^2 $](http://www.candlish.net/wp-content/latex/bbc/bbcb748a212e688f98848c74e7eea8ca-ffffff-000000-0.png)
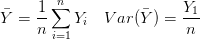
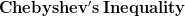
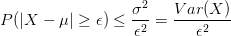
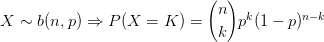
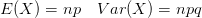
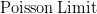
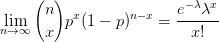
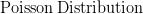
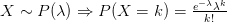
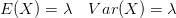
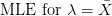
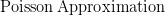
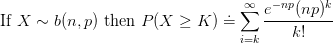
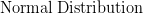
![$ X \sim N( \mu, \sigma^2 ) \Rightarrow P( a < X < b ) = {\displaystyle \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}\sigma} \int_{a}^{b}e^{\frac{-1}{2}[(x-\mu)/\sigma]^2} dx} $ $ X \sim N( \mu, \sigma^2 ) \Rightarrow P( a < X < b ) = {\displaystyle \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}\sigma} \int_{a}^{b}e^{\frac{-1}{2}[(x-\mu)/\sigma]^2} dx} $](http://www.candlish.net/wp-content/latex/596/59672641fec8acf89a8a44ef29027f3d-ffffff-000000-0.png)
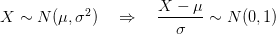
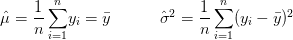
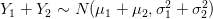

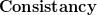
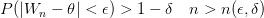
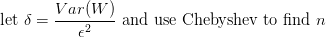
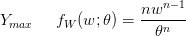
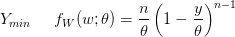
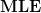
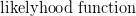
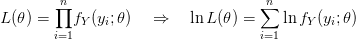
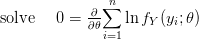
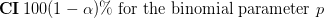
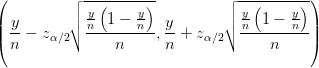
So yes, WordPress does  , but it is finicky and missing a lot of functionality. If you try to use
, but it is finicky and missing a lot of functionality. If you try to use  that doesn’t work inside the math environment (such as begin{align} ... end{align}), it wont parse. Also, you need to use the displaystlye keyword judiciously.
that doesn’t work inside the math environment (such as begin{align} ... end{align}), it wont parse. Also, you need to use the displaystlye keyword judiciously.
Edit: I've uninstalled JetPack and so lost its Beautiful Math feature. Therefore I've installed the WP LaTeX plugin. It is more configurable, and can offload formatting to a real  running alongside WordPress. With a little hacking I've got {align} going. Why someone thought is was sensible to limit WordPress'
running alongside WordPress. With a little hacking I've got {align} going. Why someone thought is was sensible to limit WordPress'  support to the math environment is beyond me.
support to the math environment is beyond me.
One requirement of the WP LaTeX plugin is that the WP unformatted plugin is also installed, so that the wptexturize() function can be disabled on  posts.
posts.
Why does the website say “since 1999” you might ask? Because that is when I registered the candlish.net domain and established an online presence.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
candlish@w530:~$ whois candlish.net Whois Server Version 2.0 Domain names in the .com and .net domains can now be registered with many different competing registrars. Go to http://www.internic.net for detailed information. Domain Name: CANDLISH.NET Registrar: NETWORK SOLUTIONS, LLC. Sponsoring Registrar IANA ID: 2 Whois Server: whois.networksolutions.com Referral URL: http://networksolutions.com Name Server: GW2.CANDLISH.NET Name Server: GW3.CANDLISH.NET Status: clientTransferProhibited http://www.icann.org/epp#clientTransferProhibited Updated Date: 30-jun-2013 Creation Date: 06-mar-1999 Expiration Date: 06-mar-2018 >>> Last update of whois database: Tue, 13 Oct 2015 12:37:17 GMT <<< |
How ’bout that wordwrap?
|
1 2 3 |
candlish@w530:~$ for i in {1..72}; do echo -n $(($i %10)); done; echo 123456789012345678901234567890123456789012345678901234567890123456789012 candlish@w530:~$ |
Fairly narrow layout. :/